When choosing an air conditioning system or heat pump, efficiency is one of the most important factors to consider. That’s where SEER rating comes in. SEER, or Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, measures how efficiently an air conditioning system or heat pump operates over an entire cooling season. Understanding SEER ratings can help homeowners and businesses make informed decisions that lead to lower energy bills, reduced environmental impact, and greater overall comfort.
Understanding SEER Ratings
SEER is calculated by dividing the total cooling output (measured in British Thermal Units or BTUs) by the total energy consumed (measured in watt-hours) over a typical cooling season. The higher the SEER rating, the more energy-efficient the system.
For example:
- A unit with a SEER rating of 14 will be less efficient than a unit with a SEER rating of 20.
- A higher SEER rating means the system requires less electricity to cool a space effectively.

SEER vs. EER: What’s the Difference?
While SEER measures efficiency over a full season, EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio) measures efficiency at a fixed temperature. SEER provides a more comprehensive view of efficiency since it accounts for seasonal temperature fluctuations, making it a better metric for overall performance.
Why Does SEER Rating Matter?
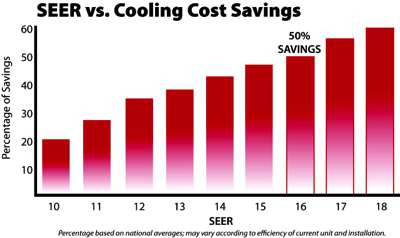
1. Lower Energy Bills
Higher SEER ratings translate to lower electricity consumption, reducing energy bills significantly over time. Homeowners investing in high-SEER systems can see substantial long-term savings, especially in warmer climates where AC usage is high.
2. Environmental Benefits
Energy-efficient systems reduce overall power demand, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions. A high-SEER air conditioner uses less electricity, helping to minimize your home’s carbon footprint.
3. Enhanced Comfort Levels
Units with higher SEER ratings typically include advanced features such as variable-speed compressors and multi-stage cooling, allowing for more consistent temperatures, better humidity control, and quieter operation.
4. Compliance With Regulations
- In the U.S., minimum SEER requirements vary by region.
- Northern states: Minimum SEER rating of 14 for new central air systems.
- Southern & Southwestern states: Minimum SEER rating of 15 due to higher cooling demands.
- New regulations in 2023 have increased the required minimum SEER ratings, encouraging more energy-efficient technology adoption.
5. Higher Resale Value
Homes with high-SEER HVAC systems tend to attract more buyers since energy efficiency is a top priority for modern homebuyers. Installing a high-SEER system can boost a home’s marketability and long-term value.
Choosing the Right SEER Rating for Your Home
The ideal SEER rating depends on climate, usage, and budget. Here are some general recommendations:
- Mild climates: SEER 14-16 is sufficient.
- Hot/humid climates: SEER 18+ is recommended for better efficiency.
- Long-term investment: A higher SEER system may have a higher upfront cost but provides better energy savings and comfort over time.
Conclusion
SEER rating is a crucial factor in selecting an energy-efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly cooling system. While higher SEER units may have a greater initial cost, the long-term savings, improved comfort, and environmental benefits make them a smart investment. Before making a purchase, homeowners should compare SEER ratings, consider regional requirements, and evaluate long-term savings to choose the best system for their needs.
If you're considering upgrading your HVAC system, be sure to check the SEER rating and opt for the most efficient unit within your budget. It’s an investment that pays off in lower energy bills, better home comfort, and a reduced environmental footprint!


